This week I attended a seminar by the Norwegian Environment Agency and the AMAP (Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme) about the dangers facing the Arctic region, and let me tell you, there are many! To me this fact only emphasises the importance for us to protect it. Even if most of us actually doesn't live in the Arctic, the Arctic serves as a barometer for the rest of the world on how climate change will impact us all.
Here are a few of the findings that is worth knowing about the Arctic:
- There are a lot of chemicals that ends up in the Arctic, and now that the ice is melting, we are discovering occurrences of PCB, one of the most dangerous environmental toxins, that was banned in 2005 due to its acute poisoning both for humans and animals. PCB is now resurfacing, most likely due to the ocean currents.
- The temperature in the Arctic has more than doubled in the Arctic during the last 100 years, which is why you might often hear that the climate change is happening twice as rapidly at the poles.
- 1/3 of all sea level rice will come from the Arctic region, due to melting of the polar ice caps.
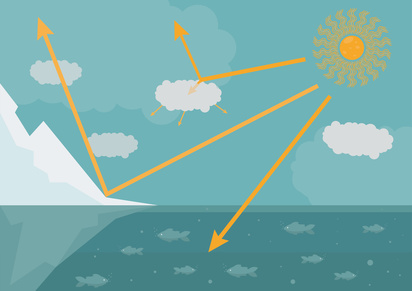
- Between 1961 and 2015, scientist have discovered that the Arctic is getting warmer, wetter, with less and thinner sea ice and less snow. This is affecting the albedo effect; how much sun is reflected back - with a white surface, a lot of the sun is reflected back, but with darker surfaces, as an ocean, the heat is adopted. To illustrate this, look at the drawing underneath.
- Earlier, there used to be a higher percentage of many year old ice. Now, that percentage has gone down, and one year old ice is more common. This affects life on a molecular level, because there are life living within the ice. This may have grave implications for the ecosystems, that we yet don't know.
- Introduced species is another threat to the biodiversity. Due to warmed temperature in the water, new species are making its way up in the Arctic. Some of these are taking over the territories to species that have spent a long time adapting to that particular climate. One example is that Atlantic cod has gone up in population, and Polar cod has decreased.
So, what can be done about this?
The advice that was given at the conference were these: The Paris agreement is important, but more needs to be done.
- Marine surveillance needs to be strengthened and we need to be prepared for the unknown.
In the former IPCC reports, the Arctic region has been under-communicated. This needs to change, because the Arctic is a very sensitive region, and as someone said at the seminar - the Arctic is everybody's business.
I hope this has provided you with some new and interesting input, although this blog post was a more science based one. A lot of exciting things will take place in the Arctic region this summer, so stay tuned for more updates on how to protect the Arctic.